Operated by the University of California for the National Nuclear Security Administration,
of the US Department of Energy. Copyright © 2001 UC | Disclaimer/Privacy
There are two origins of replication, OriL located within the UL region centered at 62,929 and OriS within repeat LTRc and LTRc' centered at 132,760 and 148,981.
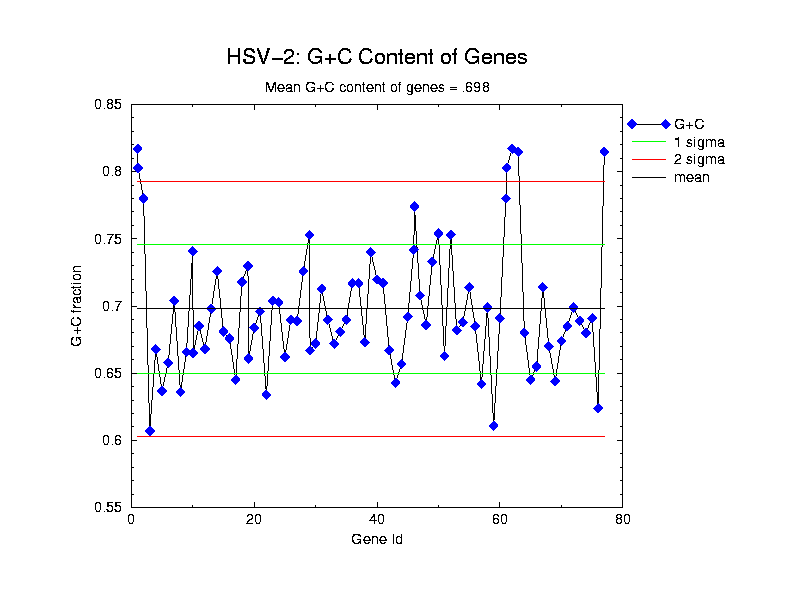
Codon usage as determined by CodonW, written by John Peden pdxjfp@molbiol.ox.ac.uk, while in the laboratory of Paul Sharp at the University of Nottingham:
Phe UUU 636 0.90 Ser UCU 159 0.36 Tyr UAU 187 0.36 Cys UGU 186 0.50
Leu UUA 41 0.06 UCA 58 0.13 TER UAA 25 0.90 TER UGA 32 1.16
UUG 261 0.38 UCG 737 1.66 UAG 26 0.94 Trp UGG 500 1.00
CUU 241 0.35 Pro CCU 187 0.19 His CAU 174 0.30 Arg CGU 210 0.32
CUC 1098 1.59 CCC 2064 2.08 CAC 975 1.70 CGC 1974 3.01
CUA 162 0.24 CCA 204 0.21 Gln CAA 172 0.27 CGA 269 0.41
CUG 2332 3.38 CCG 1513 1.53 CAG 1086 1.73 CGG 1199 1.83
Ile AUU 158 0.42 Thr ACU 66 0.11 Asn AAU 93 0.21 Ser AGU 104 0.23
AUC 872 2.31 ACC 1159 1.98 AAC 775 1.79 AGC 730 1.65
AUA 104 0.28 ACA 113 0.19 Lys AAA 169 0.49 Arg AGA 74 0.11
Met AUG 693 1.00 ACG 1000 1.71 AAG 524 1.51 AGG 210 0.32
Val GUU 281 0.37 Ala GCU 215 0.14 Asp GAU 339 0.29 Gly GGU 237 0.27
GUC 1182 1.55 GCC 3196 2.10 GAC 1976 1.71 GGC 1567 1.76
GUA 150 0.20 GCA 222 0.15 Glu GAA 391 0.37 GGA 324 0.36
GUG 1441 1.89 GCG 2441 1.61 GAG 1724 1.63 GGG 1443 1.62
43738 codons in 83 genes (used Universal Genetic code)
Current analysis of this genome shows 79 distinct genes, 4 of which have two copies for a total of 83 genes. Three of these 79 genes have intron(s) and they are gamma34.5, alpha0 and UL15. Interestingly UL16and UL17code within the intron of UL15. Nine of the genes (11%) have been assigned an EC number while ten (13%) have unknown function.
Three pairs of genes are known to be coterminal and code in frame. These include: UL8.5 and UL9, UL15 and UL15.5 and UL26 and UL26.5.
Also three pairs of genes are known to overlap completely coding on opposite strands. They are:
gamma34.5 and
Orf-P,
UL27.5 and
UL27 and
UL43 and
UL43.5.
|
LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL LABORATORY Operated by the University of California for the National Nuclear Security Administration, of the US Department of Energy. Copyright © 2001 UC | Disclaimer/Privacy |
Nina Thayer nthayer@lanl.gov Last Modified: 10/01/2001 |